What Types of Hearing Aids Are Available and Which One Is Best?
Hearing aids have advanced far beyond basic sound amplification, offering features like noise reduction, Bluetooth connectivity and personalized settings to improve daily communication. Yet many people are unsure when to seek help, how much devices cost or which type is right for their needs. This guide explains how hearing aids work, the different styles available, what to expect during the fitting process and how to choose a device that fits both hearing requirements and lifestyle.
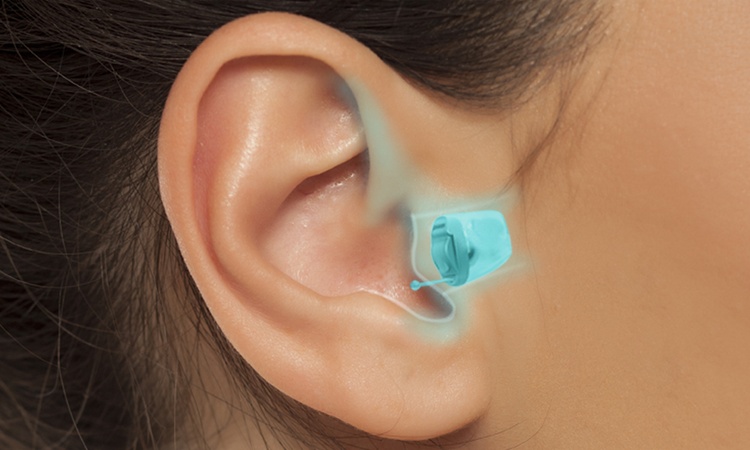
Hearing loss affects millions of people worldwide, yet many delay seeking treatment due to confusion about available options. Modern hearing aids have evolved significantly from the bulky devices of the past, now offering sophisticated technology in compact, often nearly invisible designs. Understanding the different types available and their respective benefits helps individuals make informed decisions about their hearing health.
How Hearing Aids Work and Common Types
Hearing aids function by amplifying sound waves and converting them into electrical signals that stimulate the auditory nerve. All hearing aids contain three basic components: a microphone to pick up sound, an amplifier to increase volume, and a speaker to deliver processed sound to the ear. The main types include behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), in-the-canal (ITC), completely-in-canal (CIC), and invisible-in-canal (IIC) models. BTE devices sit behind the ear with a tube connecting to an ear mold, making them suitable for various hearing loss levels. ITE models fit entirely within the outer ear, while ITC and CIC devices are progressively smaller and less visible. IIC hearing aids are the most discreet option, sitting deep within the ear canal.
Features Cost and Maintenance of Modern Hearing Aids
Contemporary hearing aids incorporate advanced features like digital noise reduction, directional microphones, Bluetooth connectivity, and smartphone app integration. Premium models offer artificial intelligence that learns user preferences and automatically adjusts to different environments. Rechargeable batteries have largely replaced disposable ones in newer models, providing convenience and environmental benefits. Regular maintenance includes daily cleaning, proper storage in dry conditions, and periodic professional servicing. Battery life varies from 3-7 days for disposable batteries to 24 hours for rechargeable units. Wax guards and filters require regular replacement to maintain optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid Based on Needs Lifestyle and Budget
Selecting appropriate hearing aids involves considering hearing loss severity, daily activities, dexterity limitations, and aesthetic preferences. Active individuals may benefit from water-resistant models with advanced noise reduction for outdoor activities. Those frequently in meetings might prioritize directional microphones and Bluetooth capabilities for phone calls. Manual dexterity affects the ability to handle smaller devices and change batteries. Lifestyle factors include frequency of social situations, work environment demands, and technology comfort level. Budget considerations extend beyond initial purchase price to include ongoing maintenance, battery costs, and potential insurance coverage.
| Hearing Aid Type | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Digital BTE | Phonak, Oticon | $1,000 - $2,500 per pair |
| Premium ITE | ReSound, Widex | $2,500 - $4,000 per pair |
| Advanced CIC | Signia, Starkey | $3,000 - $5,000 per pair |
| Rechargeable IIC | Unitron, Bernafon | $4,000 - $6,500 per pair |
| Over-the-Counter | Eargo, Lexie | $200 - $1,500 per pair |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The hearing aid market offers solutions ranging from over-the-counter options for mild hearing loss to prescription devices for severe impairment. Over-the-counter hearing aids, approved by the FDA in 2022, provide affordable alternatives for adults with mild to moderate hearing loss. These devices typically cost significantly less than prescription models but offer fewer customization options. Prescription hearing aids require professional fitting and programming, ensuring optimal performance for individual hearing profiles. Many audiologists offer trial periods, allowing users to test devices in real-world situations before committing to purchase.
Insurance coverage varies significantly, with some plans covering partial costs while others exclude hearing aids entirely. Medicare traditionally does not cover hearing aids, though some Medicare Advantage plans include benefits. Veterans may qualify for coverage through VA benefits, and some employers offer hearing aid benefits or flexible spending account options. Financing programs and payment plans help make devices more accessible, while charitable organizations sometimes provide assistance for qualifying individuals.
The “best” hearing aid depends entirely on individual circumstances rather than universal rankings. Factors include degree of hearing loss, ear canal shape, lifestyle demands, technology preferences, and budget constraints. Professional audiological evaluation remains essential for determining appropriate options and ensuring proper fitting. Regular follow-up appointments optimize performance and address any concerns that arise during the adjustment period.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.