Colon Cancer Treatment: Understanding Symptoms, Early Detection, and Care Options
Colon cancer is a serious health concern that affects thousands of people each year. As with many forms of cancer, early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes. This article will explore the various aspects of colon cancer, including its symptoms, methods for early detection, and available treatment options. By understanding these key elements, individuals can be better prepared to recognize potential warning signs and seek timely medical attention.
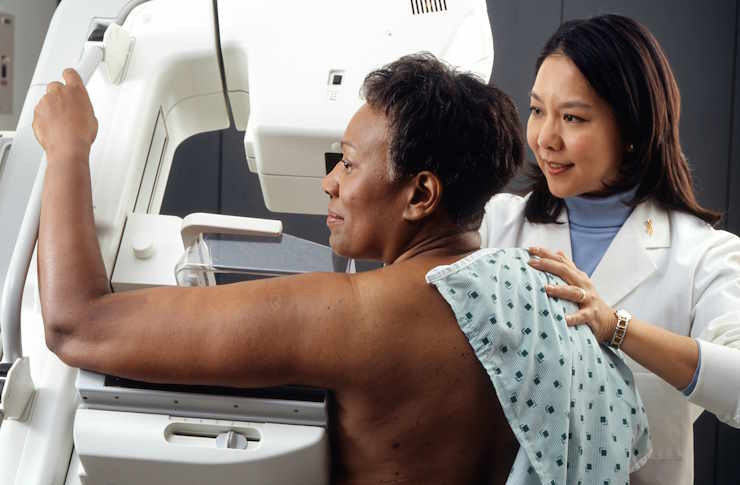
What Are the Common Symptoms of Colon Cancer?
Recognizing the signs of colon cancer is vital for early intervention. Common symptoms include persistent changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation lasting more than a few days. Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool, whether bright red or very dark, should never be ignored. Other warning signs include unexplained weight loss, constant fatigue, and ongoing abdominal discomfort, such as cramps, gas, or pain. Many people also experience a feeling that their bowel doesn’t empty completely.
How Is Colon Cancer Detected in Its Early Stages?
Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. The primary screening method is colonoscopy, which allows doctors to examine the entire colon and remove potentially cancerous polyps before they develop into cancer. Other detection methods include flexible sigmoidoscopy, which examines the lower colon, and stool-based tests that check for blood or DNA markers. CT colonography, also known as virtual colonoscopy, provides detailed images of the colon without requiring an invasive procedure.
What Are the Early Signs That Shouldn’t Be Ignored?
While some symptoms may seem minor, certain signs warrant immediate medical attention. Unexplained anemia, especially in men or postmenopausal women, can indicate internal bleeding from a tumor. Changes in stool shape, particularly narrow or ribbon-like stools, might suggest a growth constricting the bowel passage. Persistent abdominal bloating or unusual discomfort after eating should also prompt medical evaluation, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Colon Cancer?
Treatment approaches vary depending on the cancer stage and individual patient factors. Surgery remains the primary treatment for localized colon cancer, with procedures ranging from polypectomy for early-stage tumors to partial colectomy for more advanced cases. Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery, particularly for stage III and IV cancers. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy represent newer treatment options that can be particularly effective for specific types of colon cancer.
How Does Colon Cancer Screening Differ Across Countries?
Screening protocols vary significantly worldwide. In the United States, regular screening is recommended starting at age 45 for average-risk individuals, while many European countries begin at age 50. The frequency and preferred screening methods also differ. For example, some countries primarily rely on fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) as an initial screening tool, while others emphasize colonoscopy as the primary screening method.
Treatment Centers and Screening Options Comparison
| Treatment Center Type | Primary Screening Methods | Average Wait Time |
|---|---|---|
| Major Cancer Centers | Colonoscopy, CT Colonography | 1-2 weeks |
| Community Hospitals | Colonoscopy, FIT Testing | 2-4 weeks |
| Private Clinics | Flexible Sigmoidoscopy, Stool Tests | 1-3 weeks |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Colon cancer treatment continues to evolve with advancing medical technology and research. The key to successful outcomes lies in early detection through regular screening and prompt attention to warning signs. While treatment options have expanded significantly in recent years, prevention and early intervention remain the most effective strategies for managing this disease.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.